What is a Misdemeanor?
A misdemeanor is a type of criminal offense that is generally considered less severe than a felony. In the legal system, crimes are categorized based on their severity, with misdemeanors sitting between minor infractions and serious felonies. Misdemeanors typically involve less serious conduct and are punishable by less severe penalties. These offenses are usually punishable by fines, probation, community service, or imprisonment for up to one year in a local or county jail. Understanding what constitutes a misdemeanor is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the legal system or simply wanting to be informed citizens. In this article, we will delve into the nuances of misdemeanors and how they differ from other types of crime.
Common Examples of Misdemeanors
There are many types of misdemeanors, and they can vary significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Common examples include petty theft, simple assault, vandalism, public intoxication, disorderly conduct, and trespassing. Traffic offenses such as driving under the influence (DUI) or driving without a valid license may also be classified as misdemeanors in some areas. It's important to note that the classification of these offenses as misdemeanors can depend on factors such as the value of stolen goods, the extent of damage caused, or whether the offender has prior convictions.
Why Does Classification Matter?
The classification of a crime as a misdemeanor rather than a felony has significant implications for the accused individual. Misdemeanors generally carry lighter sentences and may not result in a permanent criminal record, depending on the jurisdiction and specific circumstances. This can affect an individual's future employment prospects, ability to obtain housing, and other aspects of life. Additionally, the legal procedures for handling misdemeanors are often less formal and less costly than those for felonies, which can save time and resources for both the defendant and the legal system.
The Legal Process for Misdemeanors
The process for handling misdemeanors typically begins with an arrest or citation. The accused will then be required to appear in court, where they may plead guilty, not guilty, or no contest. If the defendant pleads not guilty, a trial may be scheduled to determine their guilt or innocence. In many cases, especially for first-time offenders, plea bargains may be offered. A plea bargain involves the defendant agreeing to plead guilty to a lesser charge in exchange for a reduced sentence. This can expedite the legal process and result in a more favorable outcome for the defendant.
Penalties and Sentencing for Misdemeanors
The penalties for misdemeanors vary widely depending on the nature of the offense, the jurisdiction, and the defendant's prior criminal history. Common penalties include fines, probation, community service, and short-term incarceration in a local jail. In some cases, offenders may be required to attend educational programs or counseling sessions as part of their sentence. Probation is a common alternative to incarceration, allowing the offender to remain in the community under the supervision of a probation officer while complying with certain conditions. Failure to adhere to the terms of probation can result in additional penalties, including jail time.
The Impact of Prior Convictions
An individual's prior criminal history can significantly affect the sentencing for a misdemeanor. Repeat offenders may face harsher penalties, including longer jail sentences or higher fines, than first-time offenders. Some jurisdictions have "three strikes" laws that impose mandatory minimum sentences for individuals with multiple convictions, even if the offenses are misdemeanors. It's essential for defendants to be aware of how their criminal record may influence their case and to seek legal advice if they have concerns about potential penalties.
The Role of Legal Representation
Having competent legal representation is crucial for anyone facing misdemeanor charges. An experienced attorney can provide valuable guidance throughout the legal process, help negotiate plea deals, and advocate for the best possible outcome. Public defenders are available for individuals who cannot afford private counsel, ensuring that everyone has access to legal representation. Whether through a public defender or private attorney, legal counsel can help defendants understand their rights, navigate the complexities of the legal system, and make informed decisions about their case.
Expungement and Record Sealing
One of the benefits of misdemeanor classification is the potential for expungement or record sealing. Many jurisdictions allow individuals to petition for their misdemeanor record to be sealed or expunged after a certain period, provided they meet specific criteria. This can remove the conviction from public records, making it easier for individuals to secure employment, housing, and other opportunities. The process for expungement or record sealing varies by jurisdiction, and consulting with an attorney can help individuals understand their eligibility and navigate the application process.
Understanding the Differences Between Misdemeanors and Felonies
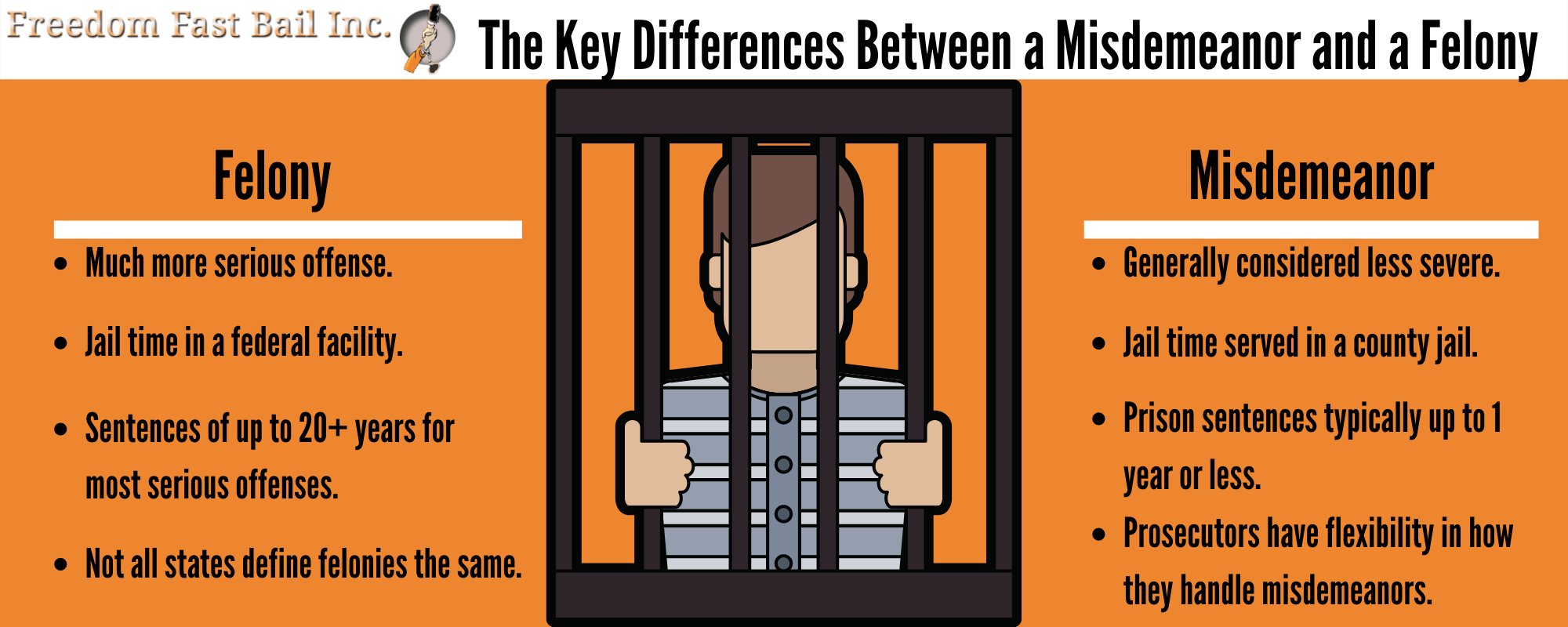
While both misdemeanors and felonies are criminal offenses, they differ significantly in terms of severity, legal procedures, and potential penalties. Felonies are more serious crimes that are punishable by more than a year in state prison, larger fines, or even the death penalty in some jurisdictions. Examples of felonies include murder, rape, robbery, and serious drug offenses. Misdemeanors, on the other hand, are less severe and typically involve penalties that are less life-altering. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone navigating the legal system, as it affects everything from legal representation to sentencing and the possibility of expungement.
Conclusion: Navigating the Misdemeanor Landscape
Misdemeanors are an important category of criminal offenses that affect many people in various ways. Understanding what constitutes a misdemeanor, the legal process involved, and the potential consequences can empower individuals to make informed decisions if they find themselves facing such charges. While misdemeanors are less severe than felonies, they can still have significant implications for one's personal and professional life. By seeking proper legal representation and understanding their rights, individuals can navigate the misdemeanor landscape more effectively and work towards a positive resolution. In 2024, staying informed about these legal nuances remains crucial for anyone involved in or concerned about the criminal justice system.
You Might Also Like
Define Entrepreneur: Understanding The Modern Innovator In 2024Exploring The Maps Protocol: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024
The Enduring Charm Of Terence Hill: A 2024 Retrospective
McAfee: A Comprehensive Guide To Maximizing Your Digital Security In 2024
Exploring The New EEG: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024
Article Recommendations
- All You Need To Know About Bill Burkett Edenpure A Complete Guide
- Top Megan Fox Pics Unforgettable Looks
- Exploring Geoff Wilsons Net Worth A Comprehensive Insight