Introduction to Piaget's Theory
Jean Piaget, a renowned Swiss psychologist, revolutionized our understanding of child development with his theory of cognitive development. His work has become a cornerstone in the field of developmental psychology, offering insights into how children perceive and interact with the world. Piaget's theory emphasizes the importance of stages in cognitive development, suggesting that children move through distinct phases as they grow. These stages are characterized by different abilities and ways of thinking, which are critical to understanding how learning and intelligence evolve over time. In 2024, Piaget's theory remains a vital framework for educators, psychologists, and parents alike, providing a roadmap for nurturing a child's cognitive growth.
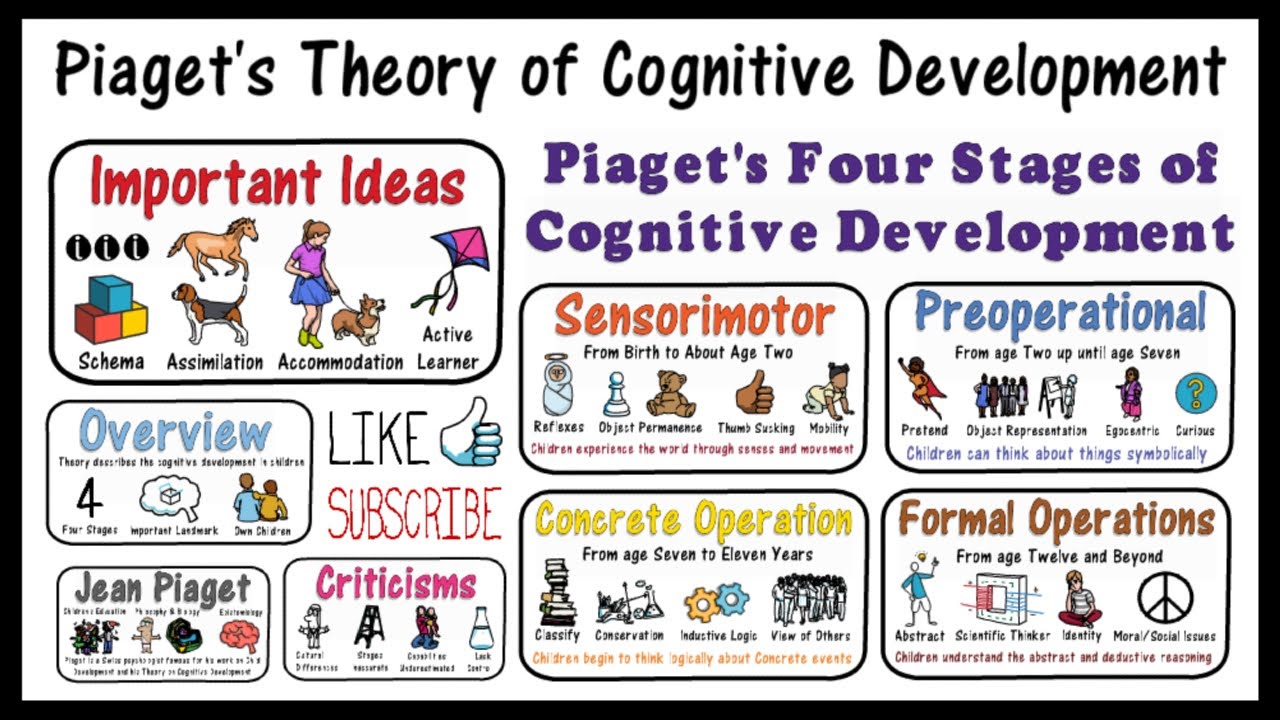
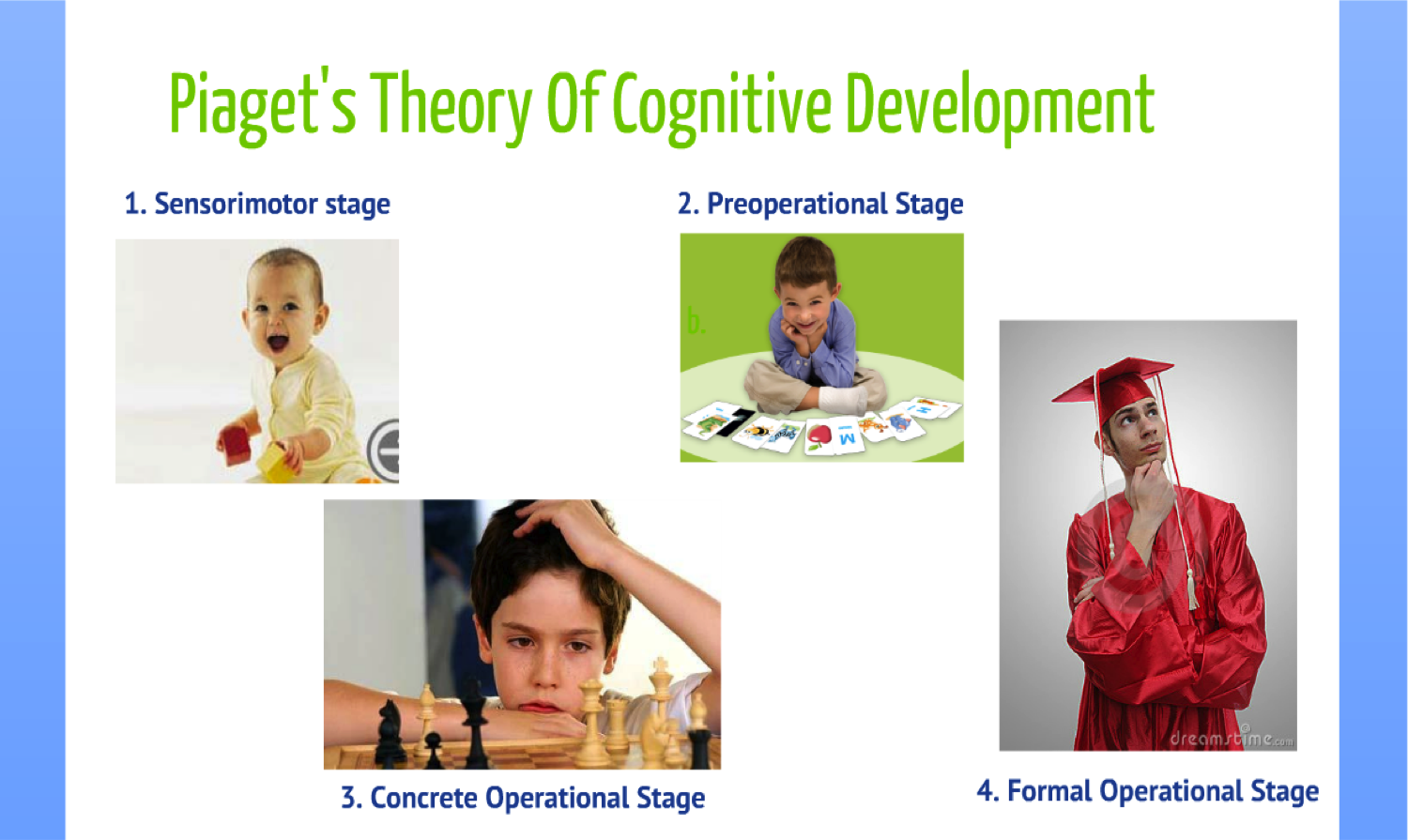
The Four Stages of Cognitive Development
Piaget's theory is built around four key stages of cognitive development: sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational. Each stage represents a new way of thinking and understanding the world. The sensorimotor stage, spanning from birth to approximately two years old, is where infants learn about their environment through sensory experiences and motor activities. As children enter the preoperational stage, from ages two to seven, they begin to develop memory and imagination, yet struggle with logic and understanding other perspectives. The concrete operational stage, from ages seven to eleven, marks the development of logical thought and the understanding of complex concepts like time and space. Finally, the formal operational stage, starting at about age twelve, is when abstract and hypothetical thinking becomes possible. Each stage is crucial for developing the cognitive abilities needed for adulthood.
Why Piaget's Theory is Still Relevant Today
In 2024, Piaget's theory continues to be relevant due to its profound insights into how children learn and develop. Despite the evolution of educational methods and psychological research, the core principles of Piaget's work remain applicable. His theory provides a foundational understanding that aids in designing age-appropriate learning experiences, ensuring that educational content aligns with children's cognitive capabilities. Moreover, Piaget's emphasis on active learning and discovery aligns well with modern educational practices that prioritize hands-on and experiential learning over rote memorization. His work encourages a more personalized approach to education, where the child's developmental stage dictates the learning process.
Applying Piaget's Theory in Educational Settings
Educators around the world have applied Piaget's theory to create effective teaching strategies that cater to the developmental stages of their students. For instance, in the sensorimotor stage, teachers focus on interactive play and exploration to stimulate learning. In the preoperational stage, educators use visual aids and storytelling to enhance memory and creativity. During the concrete operational stage, hands-on activities and experiments help students understand complex concepts. In the formal operational stage, educators challenge students with abstract problems and encourage critical thinking. By aligning teaching methods with Piaget's stages, educators can foster an environment where students thrive cognitively and emotionally.
Criticisms and Limitations of Piaget's Theory
While Piaget's theory has been influential, it is not without its criticisms. Some researchers argue that Piaget underestimated children's cognitive abilities, suggesting that his stage-based approach is too rigid. Critics also highlight that Piaget's theory does not account for cultural and social influences on cognitive development, which can play a significant role in shaping a child's learning experience. Additionally, more recent studies suggest that cognitive development may be more continuous than stage-like, challenging the notion of distinct phases. Despite these criticisms, Piaget's theory provides a valuable framework for understanding child development, even as new research continues to expand and refine our knowledge.
The Role of Parents in Supporting Cognitive Development
Parents play a crucial role in supporting their children's cognitive development, and Piaget's theory offers valuable insights into how they can do so effectively. By understanding the stages of cognitive development, parents can tailor their interactions and activities to support their child's growth. For example, during the sensorimotor stage, parents can provide a variety of sensory experiences and opportunities for exploration. In the preoperational stage, engaging in imaginative play and asking open-ended questions can stimulate cognitive development. As children enter the concrete operational stage, parents can involve them in problem-solving activities and discussions about everyday phenomena. By aligning parenting practices with Piaget's stages, parents can foster an enriching environment that promotes cognitive growth.
Incorporating Technology in Piagetian Framework
In 2024, technology continues to play a significant role in education, and integrating it with Piaget's theory can enhance learning outcomes. Digital tools and applications can be designed to align with Piaget's stages, offering interactive experiences that promote cognitive development. For instance, apps that encourage exploration and experimentation can be beneficial during the sensorimotor stage. Educational games that enhance memory and imagination can support the preoperational stage. Virtual simulations and problem-solving platforms can aid in the concrete operational stage, while online forums and collaborative projects can foster abstract thinking in the formal operational stage. By thoughtfully incorporating technology, educators and parents can create dynamic learning environments that align with Piaget's principles.
Research Advancements in Cognitive Development
Recent advancements in cognitive development research continue to build upon and expand Piaget's foundational work. Neuroscience has provided deeper insights into how the brain develops, offering new perspectives on cognitive processes. These findings have led to a better understanding of the biological underpinnings of cognitive development and how they interact with environmental factors. Additionally, cross-cultural studies have highlighted the diversity in developmental pathways, emphasizing the need for a more inclusive approach to understanding cognitive growth. While Piaget's theory remains a critical framework, ongoing research is essential for refining our understanding of cognitive development and applying it effectively in diverse contexts.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of Piaget's Theory
As we navigate the complexities of education and child development in 2024, Piaget's theory stands as a testament to the enduring significance of understanding cognitive development. His insights have shaped educational practices and parenting strategies, providing a foundation for nurturing young minds. While the theory has evolved over time, its core principles continue to guide educators, psychologists, and parents in fostering environments that support cognitive growth. As research progresses and new technologies emerge, Piaget's work will undoubtedly continue to inspire and inform our approaches to teaching and learning. By embracing the wisdom of Piaget's theory, we can equip future generations with the cognitive tools they need to thrive in an ever-changing world.
You Might Also Like
Understanding Uber Stocks In 2024: A Comprehensive GuideUnderstanding The True Meaning Of Power In 2024
Exploring The Magic Of Barbie Films: A Journey Through Animation And Fantasy In 2024
Understanding Photosynthesis: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024
Exploring The World Of Website Templates: A 2024 Guide
Article Recommendations
- Diving Deep Into The Life And Wealth Of Albert Preciado
- Exploring The Fascinating Journey Of Gorilla Glue Girl Net Worth
- Ct Fletcher Net Worth A Look Into The Life And Wealth Of The Iron Addict