Introduction to TCP Layers
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is a fundamental protocol within the suite of Internet protocols. It is responsible for ensuring reliable communication between different devices on a network. In essence, TCP helps in the successful transmission of data packets from one point to another, establishing a connection that guarantees data integrity and order. As we advance further into 2024, understanding the intricacies of TCP layers becomes crucial for network administrators, IT professionals, and even tech enthusiasts. This article aims to demystify TCP layers, exploring their significance, functionality, and how they contribute to seamless internet communication.
The Role of TCP in Internet Communication
TCP operates at the transport layer of the Internet Protocol Suite, which is commonly referred to as the TCP/IP model. This layer is pivotal because it provides end-to-end communication services for applications. TCP ensures that data is sent and received accurately and in the correct order, which is crucial for applications like web browsing, email, and file transfers. Without TCP, our daily online interactions would be prone to errors, data loss, and inefficiencies. As such, TCP not only facilitates communication but also enhances the overall user experience by ensuring data reliability and integrity.
Breaking Down the TCP Layers
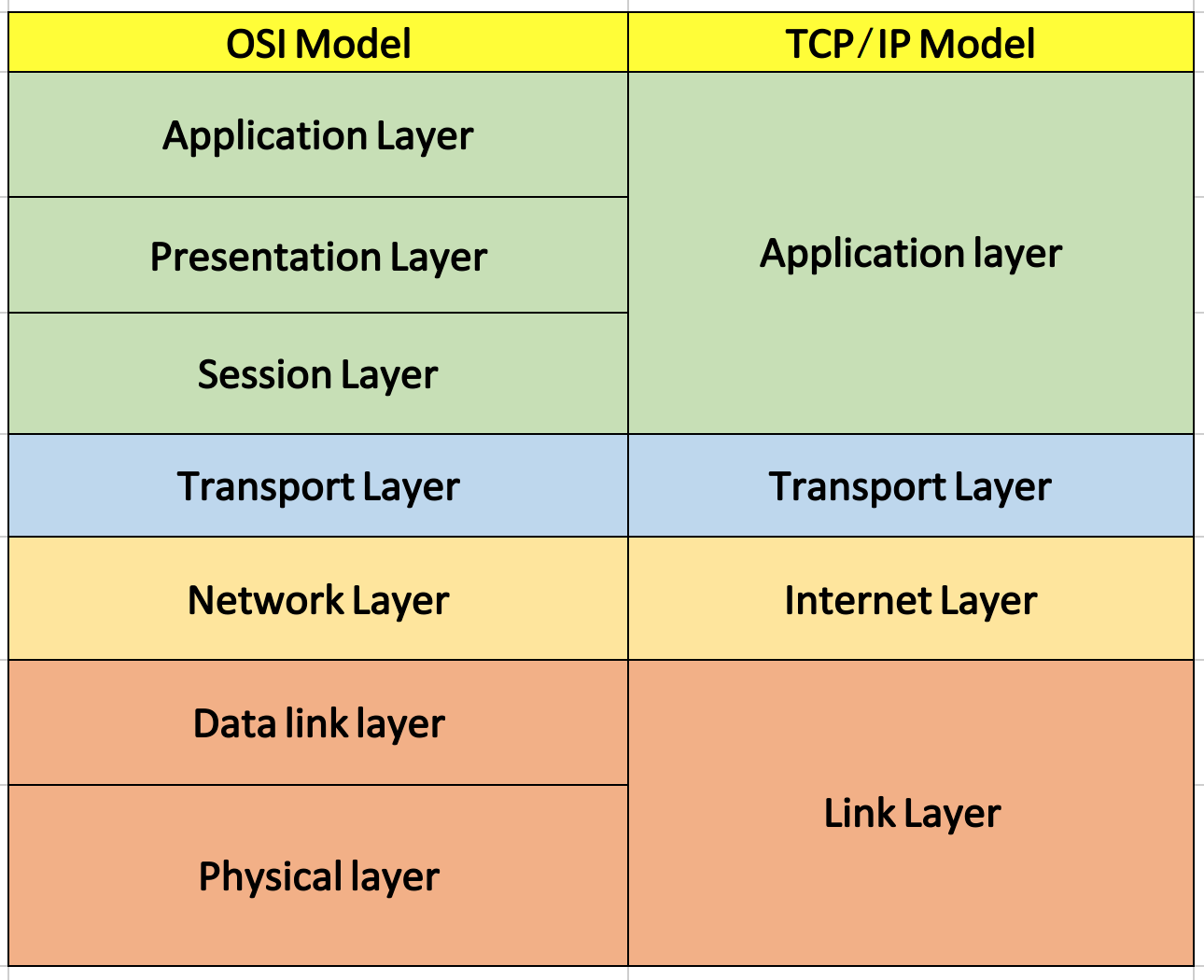
To fully grasp TCP's functionality, it's essential to understand its layered architecture. TCP is part of the four-layer model, which includes the application layer, transport layer, internet layer, and network interface layer. Each of these layers has distinct responsibilities, working in conjunction to enable seamless data transmission. The application layer is where user interaction occurs, with protocols like HTTP and FTP. The transport layer, where TCP resides, manages data flow and error recovery. The internet layer handles packet routing, while the network interface layer deals with physical data transmission. This layered approach allows for modular design and troubleshooting, making TCP both robust and versatile.
Key Features of TCP
TCP is renowned for its reliability, which is achieved through several key features. One of the most crucial features is error detection and correction. TCP uses checksums to verify data integrity, ensuring that any corrupted packets are identified and retransmitted. Another important feature is flow control, which manages the rate of data transmission between devices to prevent network congestion. Additionally, TCP supports multiplexing, allowing multiple connections to exist simultaneously between the same devices. These features, among others, make TCP an indispensable component of modern networking, providing a stable foundation for various internet applications and services.
Understanding the TCP Three-Way Handshake
The three-way handshake is a fundamental concept in TCP communication, establishing a connection between a client and a server. This process involves three steps: SYN, SYN-ACK, and ACK. Initially, the client sends a SYN (synchronize) packet to the server, indicating a request to establish a connection. The server responds with a SYN-ACK (synchronize-acknowledge) packet, acknowledging the request and providing its own synchronization. Finally, the client sends an ACK (acknowledge) packet, confirming the establishment of the connection. This handshake ensures that both parties are ready to communicate, setting the stage for reliable data transmission.
TCP vs. UDP: Understanding the Differences
While TCP is known for its reliability, it's important to understand its counterpart, the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Unlike TCP, UDP is connectionless and does not guarantee data delivery, making it faster but less reliable. UDP is often used in applications where speed is more critical than reliability, such as video streaming and online gaming. In contrast, TCP is preferred for applications where data integrity and order are paramount. Understanding the differences between these two protocols helps in selecting the appropriate one for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and user satisfaction.
The Importance of TCP Congestion Control
Congestion control is a crucial aspect of TCP, preventing network congestion and ensuring efficient data transmission. TCP employs various algorithms, such as slow start, congestion avoidance, and fast retransmit, to manage traffic and avoid congestion. These algorithms dynamically adjust the rate of data transmission based on network conditions, ensuring that the network's capacity is not exceeded. As networks continue to evolve and handle increasing amounts of data, effective congestion control becomes increasingly vital. TCP's ability to adapt to changing network conditions makes it indispensable for maintaining smooth and efficient communication.
Security Considerations for TCP
While TCP is robust and reliable, it is not immune to security threats. Common vulnerabilities include SYN flooding, where an attacker overwhelms a server with connection requests, and TCP session hijacking, where an attacker intercepts and alters communication between two parties. To mitigate these threats, additional security measures are often implemented, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols like TLS. As cyber threats continue to evolve, understanding and addressing TCP's security considerations is essential for maintaining secure and trustworthy network communication.
Future Developments in TCP
As we move further into 2024, TCP continues to evolve to meet the demands of modern networking. One notable development is the exploration of TCP alternatives, such as QUIC, which aims to improve performance over TCP by reducing latency and enhancing security. Additionally, ongoing research focuses on optimizing congestion control algorithms to accommodate the growing volume of internet traffic. These advancements highlight the ongoing efforts to enhance TCP's capabilities, ensuring it remains a cornerstone of reliable and efficient internet communication in the years to come.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of TCP
In conclusion, TCP remains a vital component of the Internet Protocol Suite, providing essential services that enable reliable and efficient communication. Its layered architecture, combined with its robust features, ensures data integrity and order, making it indispensable for a wide range of applications. As technology continues to advance, TCP evolves to meet new challenges, maintaining its relevance in the ever-changing landscape of networking. Understanding TCP layers and their functionality is crucial for anyone involved in the field of networking, ensuring that they can effectively manage and optimize network communication in 2024 and beyond.
You Might Also Like
Exploring The Legend Of The Headless Horseman In 2024The Fury: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding And Mastering It In 2024
The Ultimate Guide To Achieving Deep Sleep In 2024
Understanding And Managing Extreme Nervousness: A 2024 Guide
Understanding Downdetector Messenger: A Guide For 2024
Article Recommendations
- Jeff Allen Tami Mishler A Story Of Love Comedy And Inspiration
- Georgias Rule Cast Meet The Stars
- Expecting A Baby Ashantis Pregnancy Journey