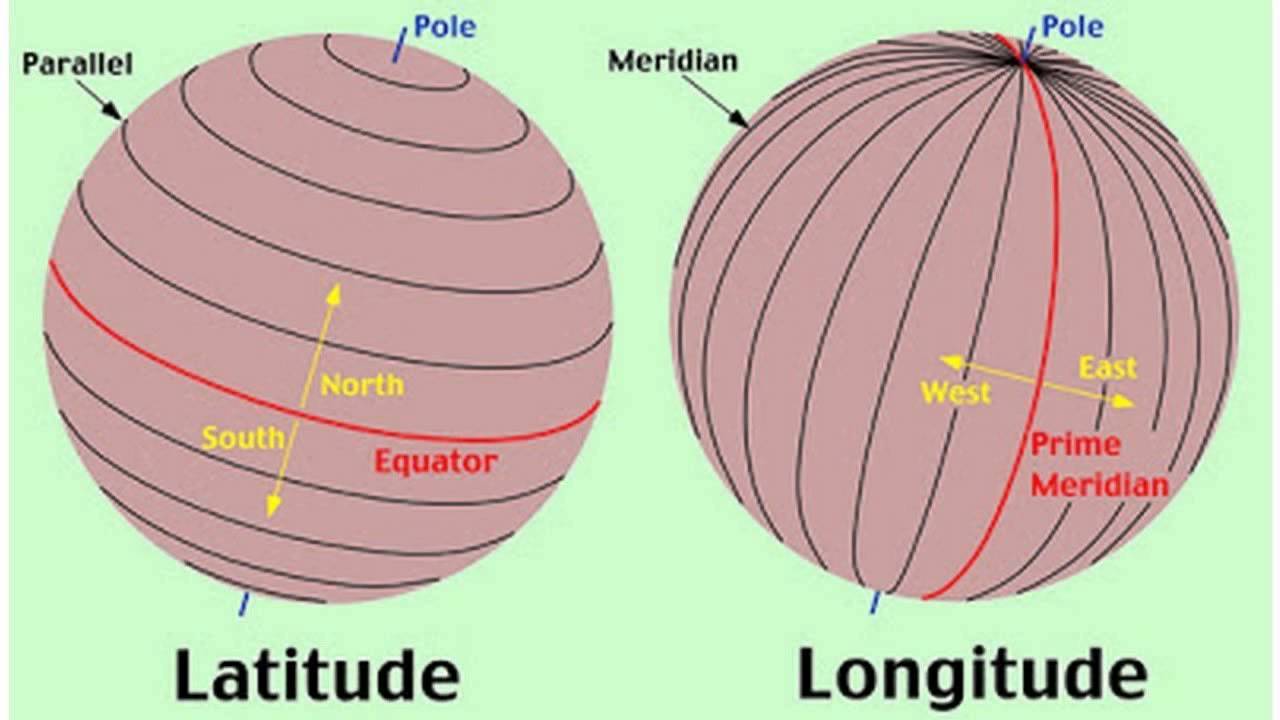
What is Latitude?
Latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the Earth's surface. It is an essential concept in geography, navigation, and mapping. Latitude is measured in degrees, ranging from 0° at the Equator to 90° at the poles. The Equator is the imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude lines run parallel to the Equator and are also known as parallels. Each parallel marks a degree of latitude, with the Equator at 0° latitude, the North Pole at 90°N, and the South Pole at 90°S. Understanding latitude is crucial for various applications, including GPS technology, climate studies, and travel.
The Importance of Latitude in Navigation
Latitude plays a vital role in navigation. Before the advent of modern technology, sailors and explorers relied heavily on latitude measurements to determine their position at sea. By measuring the angle between the horizon and a celestial body, such as the sun or a star, navigators could calculate their latitude. This method, known as celestial navigation, was a critical skill for sailors for centuries. Today, latitude is still important for navigation, though GPS technology has simplified the process. GPS devices use latitude and longitude coordinates to pinpoint precise locations anywhere on Earth, making it easier for travelers and navigators to find their way.
The Relationship Between Latitude and Climate
Latitude has a significant impact on climate. Generally, regions near the Equator experience warm, tropical climates, while regions closer to the poles experience colder, polar climates. This variation in climate is due to the angle at which the sun's rays strike the Earth. Near the Equator, the sun's rays hit the Earth more directly, resulting in warmer temperatures. In contrast, near the poles, the sun's rays strike the Earth at a more oblique angle, leading to cooler temperatures. Understanding the relationship between latitude and climate is essential for studying weather patterns, agriculture, and biodiversity.
Latitude and Its Effect on Day Length
Another interesting aspect of latitude is its effect on day length. As you move away from the Equator toward the poles, the variation in day length throughout the year becomes more pronounced. At the Equator, the length of day and night remains relatively constant, with approximately 12 hours of daylight and 12 hours of darkness. However, at higher latitudes, the difference between day and night lengths can be extreme. For example, during the summer months, regions within the Arctic Circle experience the phenomenon known as the "midnight sun," where the sun remains visible for 24 hours. Conversely, during the winter months, these regions may experience prolonged periods of darkness, known as "polar night."
Latitude in Cartography and Map Making
Latitude is a fundamental element in cartography, the science of map-making. Maps use a grid system of latitude and longitude lines to represent the Earth's surface accurately. This grid system allows cartographers to create maps that are both functional and visually appealing. Latitude lines, or parallels, are drawn parallel to the Equator, while longitude lines, or meridians, run from the North Pole to the South Pole. By understanding latitude and longitude, map users can accurately determine the location of a point on a map. This knowledge is crucial for various fields, including geography, urban planning, and environmental science.
Common Misconceptions About Latitude
Despite its importance, there are several common misconceptions about latitude. One misconception is that latitude lines are of equal length. In reality, the length of latitude lines decreases as they move away from the Equator toward the poles. Another misconception is that latitude determines weather patterns. While latitude influences climate, other factors, such as altitude, ocean currents, and prevailing winds, also play significant roles in determining weather conditions. Understanding these misconceptions can help clarify the concept of latitude and its role in geography and earth science.
Latitude in Modern Technology
In today's digital age, latitude continues to play a crucial role in modern technology. With the widespread use of GPS technology, latitude and longitude coordinates have become integral to various applications. From navigation apps on smartphones to geolocation services in online platforms, latitude is a key component in determining and sharing precise locations. Moreover, latitude data is used in geographic information systems (GIS) to analyze spatial patterns and relationships. As technology continues to advance, the importance of latitude in various fields is likely to grow, making it an essential concept for future innovations.
Latitude and Its Cultural Significance
Latitude also holds cultural significance. Throughout history, different cultures have used latitude to define territories, establish trade routes, and explore new lands. The concept of latitude has influenced the development of various cultural practices, such as timekeeping and navigation. For example, the Prime Meridian, located at 0° longitude and intersecting the Equator, is a reference point for time zones worldwide. Understanding latitude's cultural significance can provide insight into how different societies have interacted with and adapted to their geographical environments over time.
Practical Applications of Latitude
Latitude has numerous practical applications in everyday life. For travelers, understanding latitude can enhance travel experiences by providing insight into the climate and daylight hours of a destination. For farmers, latitude information can help determine the best crops to plant based on the region's climate. In education, teaching students about latitude can foster a greater understanding of geography and earth science. Furthermore, latitude is used in various professional fields, such as meteorology, geology, and environmental science, to study and analyze natural phenomena.
Conclusion: The Relevance of Latitude Today
In conclusion, latitude is a fundamental geographic concept with wide-ranging applications and significance. From navigation and climate studies to modern technology and cultural practices, latitude plays a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the Earth and its systems. As we continue to explore and innovate, the relevance of latitude is likely to grow, making it an essential topic for future research and study. Whether you're a student, traveler, or professional, understanding latitude can enhance your knowledge and appreciation of the world around you.
You Might Also Like
Unlocking The Secrets Of The Masseter Muscle: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024Exploring The World Of Pron Websites: A 2024 Guide
Exploring The Envato Market: A Comprehensive Guide For 2024
Understanding H2SO4: The Powerful And Versatile Sulfuric Acid
Unlocking The Secrets Of YouTube Subscriptions In 2024
Article Recommendations
- Jami Gertz 2024 A Closer Look At Her Life Career And Impact
- Adan Canto Ethnicity A Rich Cultural Heritage And Its Influence
- Exploring The Wealth Of Carl Ivanelli An Indepth Look At His Net Worth