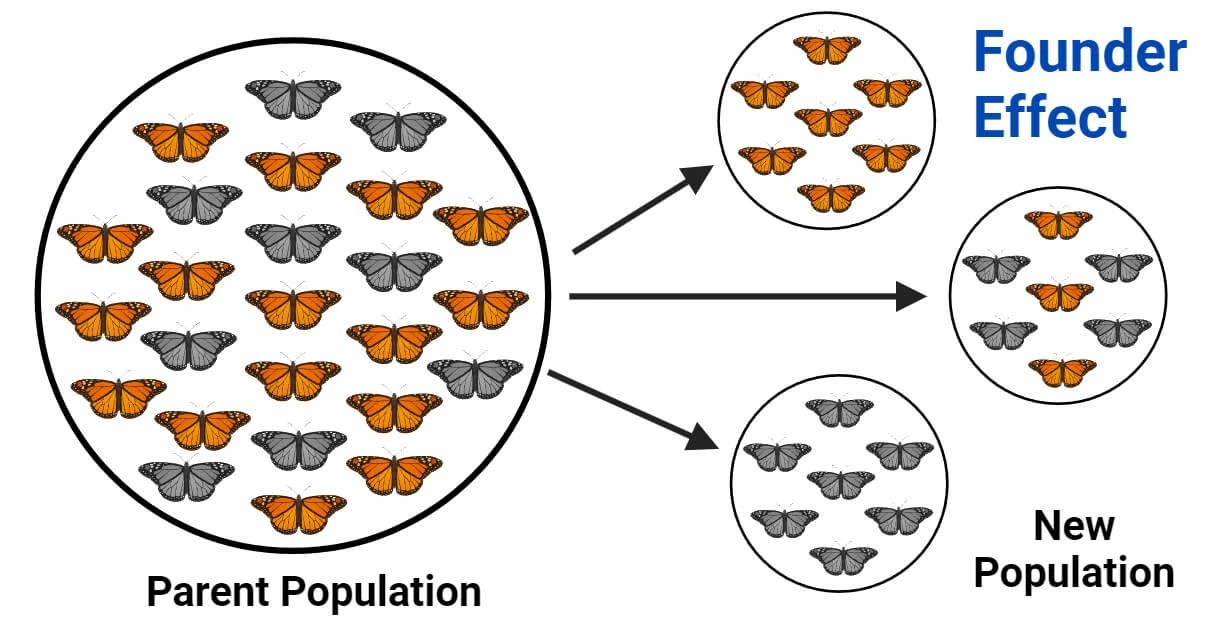
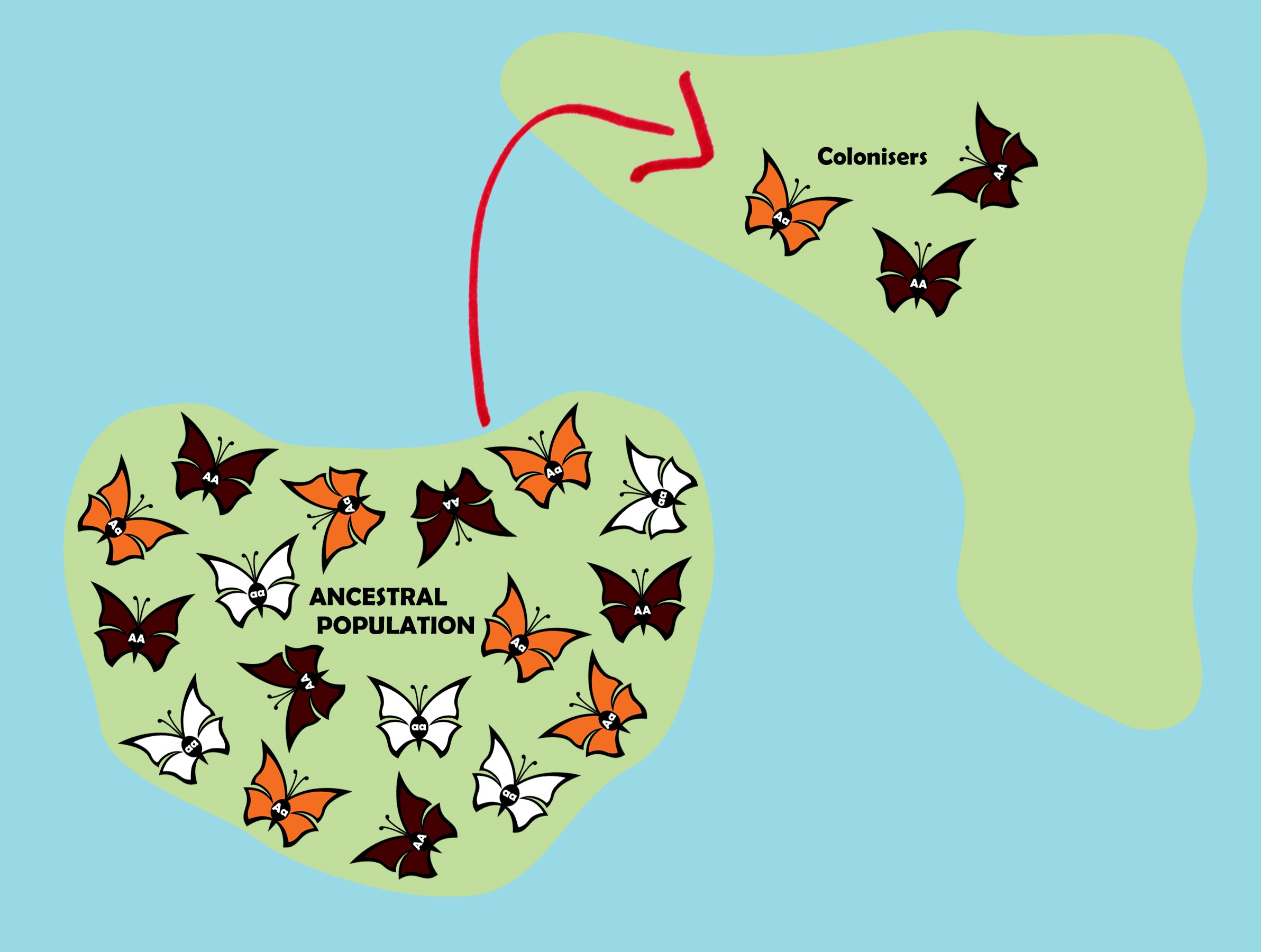
Introduction to the Founder Effect
The founder effect is a fascinating concept in evolutionary biology and genetics. It's a phenomenon that occurs when a small group of individuals becomes isolated from a larger population, leading to a new population that has reduced genetic variation compared to the original group. This can happen in various scenarios, such as when a few individuals colonize a new area or when a population is drastically reduced by a catastrophic event. The founder effect can have significant implications for the genetic diversity and adaptability of populations, influencing everything from disease susceptibility to physical traits. In 2024, understanding the founder effect is more relevant than ever, as we explore its impact on both natural ecosystems and human populations.
The Science Behind the Founder Effect
At its core, the founder effect is a type of genetic drift. Genetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies within a population, often having a more pronounced effect in small populations. When a small group becomes isolated, the genetic makeup of this group can differ significantly from the original, larger population. The alleles carried by the founders will dominate the new population, even if they were rare in the original population. This can lead to unique genetic traits becoming prevalent, which might not have been the case in a larger, more genetically diverse population. Scientists study the founder effect to understand how it influences genetic diversity and contributes to the evolution of species.
Historical Examples of the Founder Effect
Throughout history, there have been several notable examples of the founder effect. One famous case is the Amish community in the United States. The Amish originated from a small group of founders who migrated from Europe in the 18th century. Due to their relative isolation and cultural practices, the Amish population today shows a higher prevalence of certain genetic disorders that were present in the original founders. Another example can be found in the Galápagos Islands, where Darwin's finches evolved from a small group of birds that colonized the islands. These finches now exhibit a wide variety of beak shapes and sizes, adapted to different ecological niches, illustrating the founder effect's role in diversification and adaptation.
Implications of the Founder Effect on Human Health
The founder effect can have significant implications for human health, particularly in isolated populations. When a small group becomes isolated, certain genetic diseases can become more common, especially if the founding members carried alleles for those conditions. This is because the limited gene pool can lead to an increase in homozygosity, where individuals inherit two copies of the same allele. In some cases, this can result in a higher incidence of genetic disorders. Understanding the founder effect helps researchers in identifying genetic risks within populations, aiding in the development of targeted healthcare strategies and interventions. In 2024, advances in genetic research continue to shed light on how the founder effect influences human health.
The Role of the Founder Effect in Conservation Biology
Conservation biologists are particularly interested in the founder effect when it comes to preserving endangered species. When populations become fragmented or reduced to small numbers, the founder effect can lead to a loss of genetic diversity, making species more vulnerable to environmental changes and diseases. Conservation efforts often focus on maintaining or increasing genetic diversity to enhance the adaptability and survival of species. Strategies may include the introduction of new individuals to isolated populations or the creation of wildlife corridors to facilitate gene flow. In 2024, as biodiversity faces increasing threats, understanding the founder effect is crucial for effective conservation planning.
The Founder Effect in Modern Human Populations
In today's interconnected world, the founder effect can still be observed in certain human populations, particularly those that have remained isolated due to geographical, cultural, or social factors. For instance, some indigenous communities and remote island populations exhibit unique genetic traits that are the result of historical founder events. Studying these populations provides valuable insights into human evolution, migration patterns, and the impact of isolation on genetic diversity. As genetic research techniques advance, scientists in 2024 continue to explore how the founder effect shapes the genetic landscape of modern human populations.
Genetic Technologies and the Founder Effect
Advancements in genetic technologies have revolutionized our understanding of the founder effect. Tools such as whole-genome sequencing and bioinformatics allow researchers to analyze genetic variation at an unprecedented level of detail. These technologies enable the identification of specific genetic markers linked to the founder effect and the reconstruction of historical population dynamics. In 2024, researchers use these cutting-edge techniques to study both ancient and contemporary populations, uncovering the genetic legacy of founder events and their ongoing impact. As we continue to refine these technologies, the potential for new discoveries about the founder effect and its role in evolution is immense.
The Cultural Impact of the Founder Effect
Beyond its biological implications, the founder effect also has cultural dimensions. In isolated communities, unique cultural practices and traditions can emerge alongside genetic traits. These cultural elements often become intertwined with the community's identity, shaping social structures, languages, and belief systems. In 2024, anthropologists and sociologists study the interplay between genetic and cultural evolution, examining how founder events influence cultural diversity and resilience. Understanding these interactions helps us appreciate the complexity of human societies and the role of genetic and cultural factors in shaping our world.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding the Founder Effect
While the founder effect is a well-established concept, it is not without its challenges and controversies. Some researchers debate the extent to which the founder effect alone can explain patterns of genetic diversity, arguing that other factors such as natural selection and gene flow also play significant roles. Additionally, ethical considerations arise when studying human populations, particularly regarding consent and the potential for stigmatization. In 2024, scientists are increasingly aware of these issues and strive to conduct research that is both scientifically rigorous and ethically responsible. By addressing these challenges, we can continue to deepen our understanding of the founder effect and its implications.
Conclusion: The Future of Founder Effect Research
As we look to the future, the study of the founder effect promises to yield new insights into the processes that shape genetic diversity and evolution. In 2024, interdisciplinary approaches that integrate genetics, anthropology, ecology, and conservation biology are paving the way for novel discoveries. Continued research on the founder effect will enhance our ability to address pressing issues such as biodiversity loss, genetic diseases, and cultural preservation. By unraveling the complexities of the founder effect, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate tapestry of life and the forces that drive its diversity. As we continue to explore this fascinating phenomenon, the possibilities for advancing our understanding of evolution and genetics are truly exciting.
You Might Also Like
2K Gamer: A Comprehensive Guide To Enhance Your Gaming Experience In 2024Exploring Dove Ads: A Journey Through Empowering Campaigns In 2024
Lice Bug: Understanding, Prevention, And Treatment In 2024
The Comprehensive Overview Of Global Energy Production And Consumption In 2024
Understanding H2SO4: The Powerful And Versatile Sulfuric Acid
Article Recommendations
- Ryan Cameron A Pioneer In American Finance And Economic Leadership
- Georgias Rule Cast Meet The Stars
- Height Of Tori Kelly Unveiling The Facts